DENDRO THERAPEUTIC EFFECT OF PLANTINGS ON CITIZENS
DENDRO THERAPEUTIC EFFECT OF PLANTINGS ON CITIZENS
Abstract
The article presents the results of a study of the method of Gas Discharge Visualization (GDV). Advantages of GDV-bioelectrography – simplicity of execution, efficiency of obtaining results, can be successfully used in the study of the mechanisms of action not only in clinical practice, but also for the diagnosis and monitoring of the effectiveness of forest therapy on the human body. A walk in the woods is the best remedy for stress, many experts say. But how and why do "forest baths" affect us? And how can a city dweller feel the effectiveness of forest therapy? In recent years, forest therapy and "forest baths" have become so popular that many experts talk about walking in the forest as the most effective and safe medicine for stress. The obtained results of the studies conducted on the territory of Ufa indicate a positive dynamics of the emotional state of the recreant, stabilization of systolic, diastolic blood pressure and pulse after his stay in the park / forest park. Undoubtedly, in modern conditions, in order to restore well–being and recovery, get rid of stress and gain emotional balance, city residents need to pay attention to a safe and affordable method of recovery - forest therapy.
1. Introduction
It is believed that mental health problems are one of the main causes of all diseases in the world. Kotera, Richardson, & Sheffield (2020) found that walking in the woods is effective for reducing depression, anxiety, anger and stress, and the impact on anxiety is the strongest. Future research should assess whether shorter interventions will have a beneficial effect on our well-being, mental and physical. In Japan, the practice of walking through the forest has been elevated to the rank of art and has been called "shinrin-yoku" ("forest baths"). Dr. Qing Li, an associate professor at the Japanese Medical School in Tokyo and an expert in the field of forest therapy, together with colleagues conducted a series of studies that proved the healing effect of forest baths , . Studies of the influence of the natural environment on humans are directed by the works of foreign authors and on the development of the concept of training focused on the training of forest therapists . Various methods were used to measure the positive impact of the forest environment on human health. The impact of the forest environment can be measured by staying in the forest, and the negative impact on the psychological and physiological well-being of the subjects can be measured by being in an urban environment , . In this study, the influence of plantings on the mood, recovery and vitality of Ufa residents was studied. The questionnaire was filled out by the subjects before and after the walk. The results show that time spent can be useful for reducing negative moods, such as tension, fatigue, forgetfulness, irritation, or increasing the level of recuperation.
2. Research methods and principles
The research was conducted in Ufa. From an ecological point of view, Ufa is classified as a complex city, since a significant concentration of harmful industries of mechanical engineering, chemistry, petrochemistry contribute to air and water pollution more than in neighboring regions of the country. The most active air pollutants in the city are industrial and agricultural enterprises, as well as numerous vehicles.
The total emission of harmful substances by 525 nature users is 339,7 thousand tons per year . The assortment of urban plantings is represented by local flora and introduced plants. Tília cordáta, Bétula péndula, Larix sukaczewii Dylis, Pínus sylvéstris, Pópulus nígra, Pópulus nígra var. itálica dominate. Shrubby vegetation consists of 22 species, while 12 species grow in the southern part of the city, 15 species grow in the northern part. The age structure of trees is heterogeneous. The green area of the city is 38%. For the convenience of comparing and using information about the state of woody plants in environmental analyses when studying changes, the assessment of plantings was carried out, taking into account tax indicators using well-known methods. The assessment of the effect of forest air on humans was carried out by the method of rapid diagnostics of ultra-weak fields of natural radiation with a portable A-SCAN device. The results were processed in the "Excel" program.
3. Main results

Figure 1 - An example of the image of ultra-weak fields of natural radiation of respondents in an urban environment
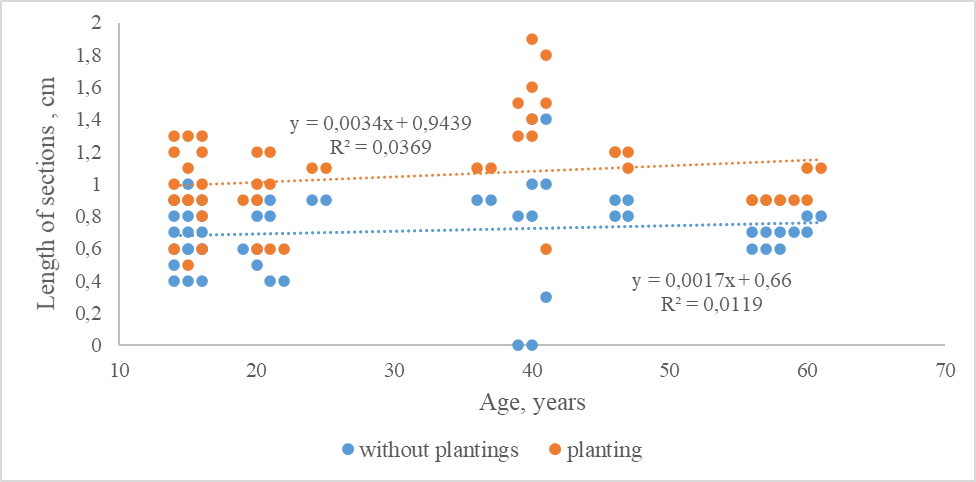
Figure 2 - The length of cross-sections over the image area of ultra-weak fields of natural radiation, depending on the location of respondents
The studies conducted to identify the influence of trees on humans have clearly shown a positive result. To determine the condition of a person, pulse and arterial (systolic and diastolic) pressure were also measured using a tonometer. According to various data, normally in adults it ranges from 60–80, 60–90 beats per minute. The number of pulse beats is equal to the heart rate (HR), i.e. normally there should be no so-called pulse deficit. In addition, the pulse is normally rhythmic, symmetrical, satisfactory filling and tension .

Figure 3 - Indicators of blood pressure and pulse measurements of respondents before and after a walk in the park
4. Discussion
According to the data of the World Health Organization (WHO): the health status of the population depends on socio-economic conditions and lifestyle (48-53%), genetic factors (18-20%), the level of development and quality of medical care (8-10%) and the degree of environmental pollution (17-20%) . Does this mean that improving the quality of the environment, in principle, can have a 2 times greater positive impact on the health of the population than the entire activity of curative medicine...? The results of the analysis on the content and influence of a number of factors on the morbidity rate of the population of Ufa are given in the work of Gabdrakhimov K.M. and Baiturina R.R. "The Influence of Forest Cover on the Health of the Population" (2020) . Currently, the GDV method has found its application in various fields of medicine , for example, a comparative assessment of diagnostic results obtained using the GDV method and traditional clinical and functional methods was carried out at the Peoples' Friendship University (branch, Sochi); a large research work was carried out at the Department of Anesthesiology and Resuscitation Military Medical Academy (VMA) of St. Petersburg , , . The same authors revealed a certain relationship between the altered mental status of the subjects and the indicators of GDV-grams, which was recorded graphically when displaying the area of the glow to the normalized area compared with the GDV-grams of practically healthy people , .
5. Conclusion
Thus, it is recommended to pay close attention to urban tree species as the main factor in improving the environment and the health of residents. In particular, this issue is vital for the elderly, children, pregnant women, citizens with a weakened immune system or predisposed to serious diseases. Green spaces, performing a sanitary and hygienic role, absorb dust and toxic gases, show a dendrotherapeutic effect on residents. They perform ecological, biological, aesthetic and health functions. With this in mind, it is necessary to bring tree plantations as close as possible to the places of everyday human life. The conducted studies are recommended for use in determining the risks to human health from significant polluting emissions of motor vehicles into the air environment and carrying out an independent assessment according to the accepted standards of concentrations of pollutants in urbanized areas. Undoubtedly, in modern conditions, in order to restore well-being and recovery, get rid of stress and gain emotional balance, city residents need to pay attention to a safe and affordable method of recovery – forest therapy. Perhaps, after some time, the doctor to whom we will come will prescribe us not pills, but communication with an oak, poplar or pine.
